by Shahnawaz Alam Finance 06 July 2023
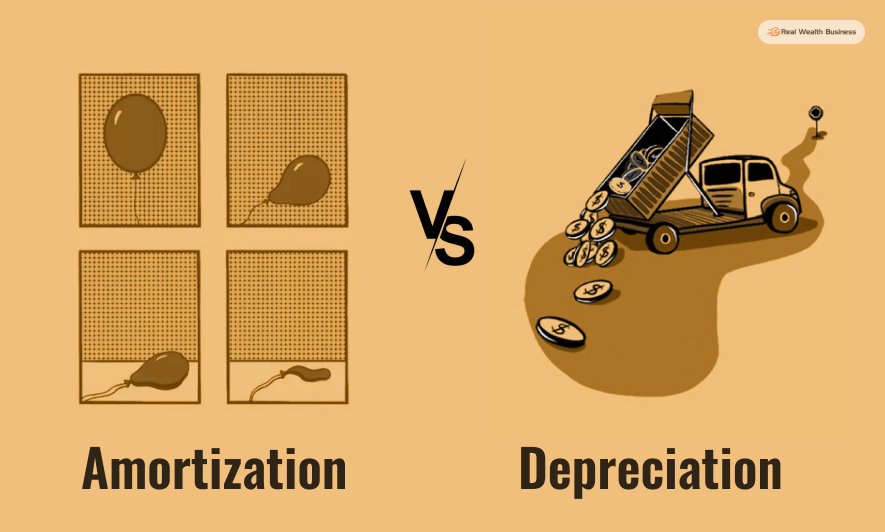
Amortization vs depreciation: what is the difference between these two accounting terms?
Whether you are an accounting student or a small business owner, it would help to know about these terms. While both of these terms mean work almost similarly, there are major differences that set them apart.
These accounting terms help businesses calculate the value of their assets at the end of a financial year. Amortization and depreciation are two methods that allow businesses to evaluate their assets.
Amortization deals with intangible assets, while depreciation helps account for tangible assets. Once you go through this article, you will know all about how these terms work and their usefulness.
Amortization Vs Depreciation: What They Mean
Since we are talking about amortization and depreciation, let’s start with the definitions of each –
📙 What Does Amortization Mean?
Not all assets a company holds are tangible or visible. Sometimes companies have digital assets such as – customer lists, trade names, franchises, patents, trademarks, copyrights, and proprietary assets. These assets have a significant level of value to a company. But they also lose their value over time. Companies record this loss in value in the financial statement. The process of accounting for these assets is amortization. You can also check out the amortization definition we talked about earlier.
While accounting for the amortization of an intangible asset, the straight-line method is usually followed.
📙 What Does Depreciation Mean?

Fixed and tangible assets lose their value over. It is inevitable for different assets like buildings, machinery, equipment, and computers to lose their value little by little. The accounting process for these tangible and fixed assets is called Depreciation.
Businesses and companies usually own many assets, which they need to account for during the end of a financial year. For such assets, when accounting, they estimate a useful life and spread their depreciation throughout the useful life. Once the asset becomes obsolete, it only has a residual value that the company can sell them for.
There are different types of assets, and each of them depreciates differently. So, as expected, their accounting processes are also different. Here are the examples –
🧧 Straight-line Depreciation: Fixed assets like machinery, buildings, and real estate properties depreciate in the straight-line method. These assets usually take more than 5 to 10 years to depreciate in value.
🧧 Declining Balance Method: Assets that quickly become obsolete get calculated in the declining balance method for depreciation. Some examples would be computers, phones, and vehicles.
🧧 Double Declining Method For Assets: Assets that depreciate quickly during their first years of useful life are fit for the Double declining method for depreciation.
🧧 Units Of Production: This accounting process is used for assets that produce a certain number of products throughout their useful life. These are usually machinery that manufactures different product units.
🧧 The Sum Of Years Digit: This is another accounting process where the residual cost, cost of the assets, and the useful life of an asset are factored.
Amortization Vs Depreciation: Similarities
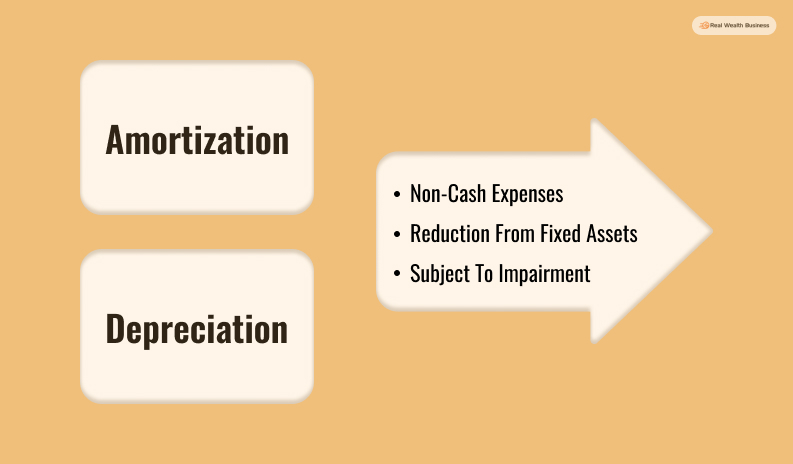
The main reason why a potential comparison of amortization vs depreciation arises is because of their existing similarities and differences. Here are some of their similarities –
📙 Non-Cash Expenses
The first similarity between amortization and depreciation is – both of these are non-cash expenses. When the expenses these expenses get recorded, companies do not face any cash reduction.
📙 Reduction From Fixed Assets
Both depreciation and amortization are counted as reductions from assets fixed in the balance sheet. These terms also get aggregated together for reporting.
📙 Subject To Impairment
Both tangible and intangible assets are subjected to impairment. So, the carrying amount of both types of assets can be written down. If something similar happens, the amortization or depreciation charges will go down. This is because there is little remaining balance to offset.
Amortization Vs Depreciation: Differences
I have listed a few points of comparison that gives you an idea about Amortization vs depreciation and how they differ.
📙 Definition
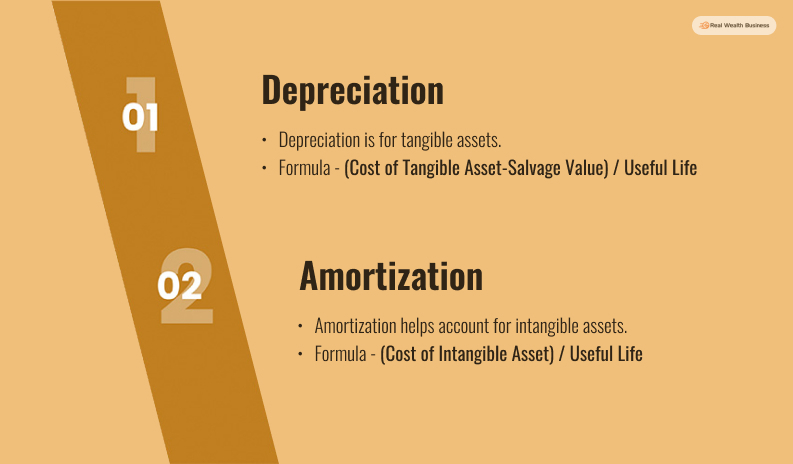
The first point of comparison is the definition. Both amortization and depreciation deal with two different types of assets. Depreciation is for tangible assets, while amortization helps account for intangible assets.
📙 Amortization Vs Depreciation Formula
One key point that creates amortization vs depreciation difference is in their accounting formula. Both amortization and depreciation have two different formulas for accounting. The difference is created because of how each asset loses their value. Tangible assets still have some scrap or residual value after depreciation. But, Intangible assets like copyrights completely lose their value after a point of time.
| Annual Amortization= (Cost of Intangible Asset)/Useful Life |
| Annual Depreciation= (Cost of Tangible Asset-Salvage Value)/Useful Life |
📙 Applicability
Amortization vs depreciation difference is also measured through how often these terms are applied. Only the tangible assets of a company are depreciated. The intangible assets are amortized.
📙 Implementation Of Different Assets
There are different types of tangible assets, and each of them depreciates differently. Due to this difference, there are different methods for depreciating. Some assets depreciate slowly and have a longer useful life, while some assets lose significant value during the initial phase of their useful life. Due to this difference in types of assets, there are five different methods for depreciation. However, for amortization, businesses usually follow the straight-line method.
📙 Residual Value
Tangible assets that depreciate have a residual value after depreciation. However, intangible assets do not have any residual value once they amortize.
📙 Purpose In Accounting
While calculating amortization vs depreciation, one should also understand the purpose behind both accounting terms. In depreciation, the cost of an asset is spread out across the time of its useful life. On the other hand, amortization helps capitalize the cost of assets over a time period. Depreciation is the accounting method for tangible assets and is useful for gaining tax benefits.
Bottom Line
Companies usually have a mix of different types of assets. These assets include tangible and intangible ones. Even within tangible assets, there are different types of assets that depreciate differently. So, it is important to know and use different accounting methods like depreciation and amortization once you understand Amortization Vs. Depreciation clearly, you will know how to use these accounting methods to work and differ.
Based on the types of assets you are accounting for, you should use the method that best suits them. However, if you have any queries, you can let us know through the comment section.
Read Also: