by Arnab Dey Technology Published on: 20 January 2023 Last Updated on: 05 March 2025

A wide area network (WAN) is a computer network that spans a large geographical area, such as a city, country, or even the world.
WANs connect smaller networks, such as local area networks (LANs) or metro area networks (MANs). WANs are typically used by organizations that need to connect multiple locations, such as businesses with various branches, or by service providers who offer connectivity to numerous customers.
The internet is the largest WAN in the world, connecting millions of computers and other devices across the globe.
How Do WANs Work?

WANs use a variety of technologies to connect networks over large distances. The most common method is to use a dedicated communication link, such as a leased line, to connect the networks. Leased lines can be either physical cables, such as copper or fiber-optic, or wireless links, such as microwave or satellite.
Another WAN method is a packet switching, where data is broken into small packets and sent over the network separately. Each packet contains routing information that allows it to be directed to its destination. The internet and many other WANs use this method.
WANs can also use a combination of technologies like VPN (Virtual Private Network), which allows them to connect remote networks over the internet using encryption securely. This method is widely used by organizations with multiple locations or remote employees who need to access internal resources.
In summary, WANs use various technologies to connect networks over large distances, such as leased lines, packet switching, or VPN. Each of these methods has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of technology depends on the organization’s or service provider’s specific requirements.
The Major Components Of WAN

The major components of a Wide Area Network (WAN) include:
- Routers: These devices are responsible for directing traffic between different networks. They use routing protocols to determine the best path for data to travel and can also perform tasks such as packet filtering and network address translation (NAT).
- Switches: These devices connect multiple devices within a network, allowing them to communicate with each other. WAN switches can be used to connect LANs or to connect a LAN to a WAN link.
- Modems: These devices are used to convert digital signals from computers into analog signals that can be transmitted over a communication link. Modems are used when the WAN link is a telephone or cable.
- Communication links are the physical connections that connect different networks. Communication links can be leased lines, such as T1 or T3 lines, or public relations, such as DSL or cable.
- Network Management System: This component is used to monitor, configure and control the network devices. It allows network administrators to troubleshoot and resolve network issues and also to perform tasks such as software upgrades and backups
- Security devices: These devices protect the network from unauthorized access and secure the data transmitted over the network. Examples of security devices include firewalls, VPNs, and intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPs).
All these components work together to provide reliable, secure, and efficient WAN connectivity for businesses and organizations.
Main Features Of WANs

The main features of Wide Area Networks (WANs) include:
1. Scalability
Scalability is a key feature of Wide Area Networks (WANs), as it allows the network to expand and accommodate additional users or locations without disrupting the existing network. This makes WANs ideal for organizations that need to connect multiple locations or remote employees.
There are different ways to achieve scalability in a WAN; some of them are:
- They are using routing protocols that support multiple paths for data to travel, automatically allowing the network to redirect traffic in case of a failure.
- Using load-balancing techniques to distribute traffic across multiple communication links can improve network performance and reduce the risk of congestion.
- Virtualization and cloud technologies allow the network to be easily scaled up or down as needed.
- Using software-defined networking (SDN) and network function virtualization (NFV) to create a more flexible and scalable network infrastructure.
By design, WANs are meant to connect multiple locations, so scalability is one of its main features, allowing the network to grow and adapt as the organization grows and adapts to its needs.
2. Reliability
Scalability is a key feature of Wide Area Networks (WANs), as it allows the network to expand and accommodate additional users or locations without disrupting the existing network. This makes WANs ideal for organizations that need to connect multiple locations or remote employees.
There are different ways to achieve scalability in a WAN; some of them are:
- Using routing protocols that support multiple paths for data to travel allows the network to redirect traffic in case of a failure automatically.
- Using load-balancing techniques to distribute traffic across multiple communication links can improve network performance and reduce the risk of congestion.
- Virtualization and cloud technologies allow the network to be easily scaled up or down as needed.
- Using software-defined networking (SDN) and network function virtualization (NFV) to create a more flexible and scalable network infrastructure.
3. Security
Security is a critical feature of Wide Area Networks (WANs) as it protects against unauthorized access and secures the data transmitted over the network. This is important for organizations that handle sensitive information or comply with HIPAA or PCI-DSS regulations.
There are different ways to achieve security in a WAN; some of them are:
- Using firewalls to block unauthorized access and control data flow in and out of the network.
- Using encryption to protect the data transmitted over the network from eavesdropping and tampering.
- Using VPN (Virtual Private Network) technology to securely connect remote networks over the internet, allowing employees to access internal resources from anywhere.
- Implementing access control mechanisms, such as role-based access control (RBAC) and network segmentation, to restrict access to sensitive resources and data.
- Implementing intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) to detect and prevent malicious activity on the network.
- Regularly updating software and security patches to prevent known vulnerabilities from being exploited.
By implementing these security measures, WANs can protect against unauthorized access, protect the data transmitted over the network and prevent malicious activity, ensuring that the network and the data it carries are secure.
Advantages Of A WAN
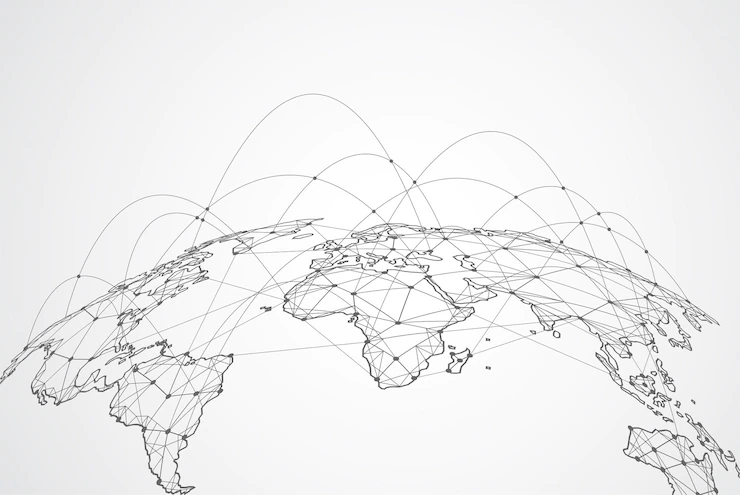
Wide Area Networks (WANs) have several advantages, including:
- Connectivity: WANs allow organizations to connect multiple locations or remote employees, enabling communication and collaboration between them.
- Increased Productivity: WANs enable employees to access resources and services from anywhere, increasing productivity and flexibility.
- Cost Savings: WANs can reduce the need for travel and increase the efficiency of business operations, resulting in cost savings for the organization.
- Improved Data Management: WANs can centralize data storage and management, making it easier to share and back up data across the organization.
- Improved Business Continuity: WANs can provide redundant communication paths and high-availability features, which can help keep the network running even in the event of a failure, thus improving business continuity.
In conclusion, WANs provide many benefits that can help organizations communicate, collaborate and share resources more effectively, increasing productivity and reducing costs while providing enhanced security and improved business continuity.
Read Also: