by Barsha Bhattacharya Finance 01 April 2025

A balance of payments is a statement that has the financial transactions taking place between the residents of a country and other parts of the world during a specific period. So, it is a very crucial method for countries to monitor international monetary transactions for a specific time frame.
Usually, the balance of payment is calculated every quarter in a calendar year.
Further, all the trades conducted in the private and public sectors are monitored and calculated in the balance of payments to understand the inflow and outflow of money to and from a country.
When a country receives the money, it is mentioned as credit in the balance of payments. Further, when a country makes payments, it is recorded as a debit.
In an ideal scenario, the balance of payments should be zero. However, in real life, it is hardly a possibility.
Thus, the balance of payments of BOP can suggest whether a country is facing a deficit or a surplus. Further, it gives us a clear picture of the direction the country is heading.
What Is The Importance Of Balance Of Payment For A Country?

The balance of payments is important for a country to assess the harmful and helpful financial and economic trends for a country.
Thus, a country can take necessary measures to improve its overall economic conditions. The following points further highlight the importance of the balance of payments in various financial and economic sectors.
- Appreciation or depreciation of the currency of a country
- Analysis and insights about transactions with other countries
What Are The Components Of Balance Of Payment?
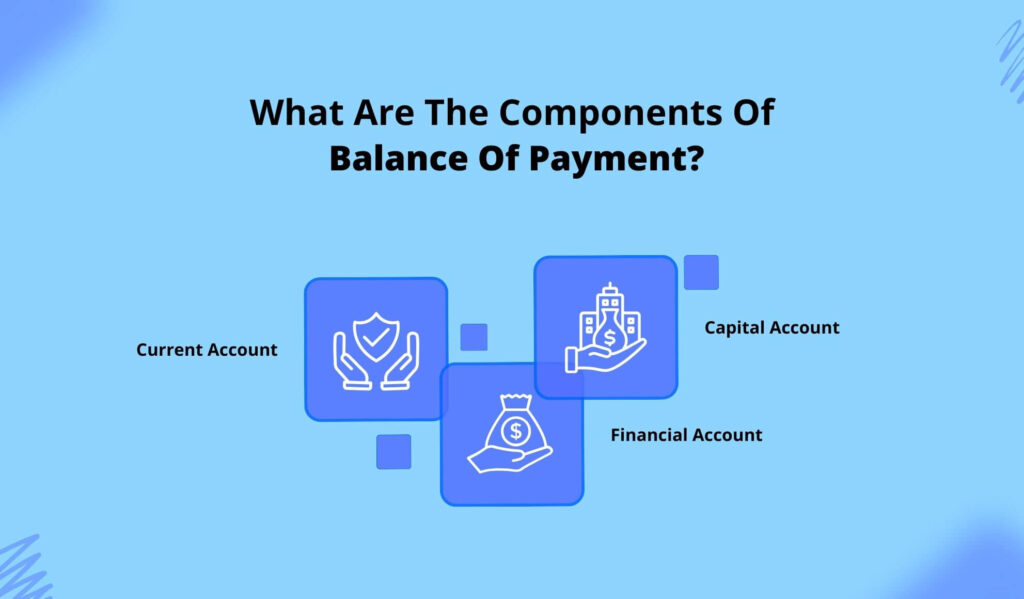
The balance of payment components are capital account, current account, and financial account. The total of capital and financial accounts should match the current account.
1. Current Account
The current account tracks the inflow and outflow of goods between countries. The exchange of services is also present in the Current Account.
Further, a current account has all the payments and receipts for raw materials and other manufacturing products.
Moreover, a current account includes:
- Business services
- Tourism
- Transportation
- Stocks
- Engineering
- Royalties from copyrights and patents
Trades and transfers take place through various categories across different countries. Trading across countries can fall under the following categories.
- Visible trade (all types of goods)
- Invisible trade (information technology and banking services)
- Other receipts/payments or unilateral transfers (donations/gifts from foreign residents/money sent to relatives in the country from foreign residents)
2. Capital Account
The capital account records all the transactions between countries. Financial, land, and property transactions are present in capital transactions.
Further, the capital account has tax flow and the sale and purchase of fixed assets by migrants to another country.
Also, the calculation or balance in the capital account is recorded through finance from the country’s capital account and vice versa.
Here are three main components of a capital account.
Investments
When a non-resident invests in corporate stocks, the fund becomes an investment.
Foreign Exchange Reserves
The central bank of a country holds foreign reserves to monitor and control the exchange rate.
Loans And Borrowings
Loans and Borrowings include different types of loans taken from public and private sectors in foreign countries.
3. Financial Account
Financial accounts the flow of funds to and from foreign countries through many investment methods such as foreign direct investments, business ventures and real estate investments.
Other components of the financial accounts are:
- Special drawing rights held with IMF (International Monetary Fund)
- Holding private assets abroad
- Gold
Therefore, financial accounts can track the changes in domestic possession of foreign products and foreign possession of domestic products.
Thus, financial accounts give us a complete picture of whether a country is buying or selling more equity, stocks, or other assets.
What Is The Formula For Calculating The Balance Of Payment?
The formula for calculating the balance of payments is easy. It is like:
Financial account+Capital account+Current account+balancing item = 0.
How Is The Balance Of Payments Balanced?
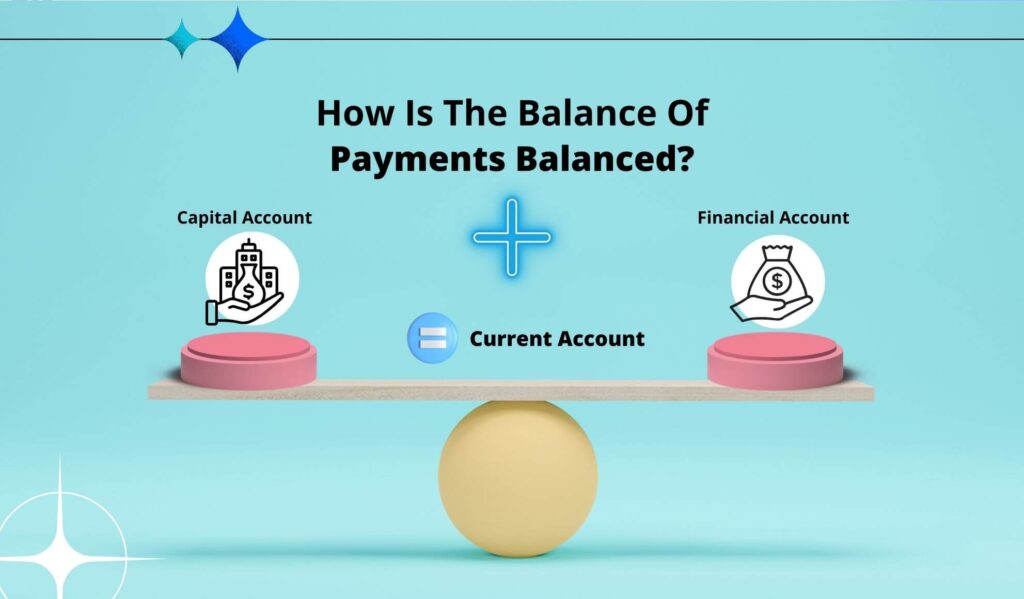
I have already mentioned that Current Account = Capital Account+ Financial Account. However, a country can hardly receive this ideal scenario.
Changing exchange rates and other variable factors impact the value of the money. As a result, balance of payments or BOP discrepancies are common.
A country may have a fixed asset abroad and that will considered as outflow in the capital account. Furthermore, when you sell the fixed asset, it will be inflow because it will be your earning against investment.
That is how discrepancies or deficits in the current accounts are funded. Furthermore, when the capital account finances a deficit in the current account, a country, in reality, is going above the capital assets for more services and goods.
In addition, a country can borrow money to fund its deficit in the current account. Then, it will be the foreign capital inflow in the balance of payments.
How Is The Balance Of Payments Liberalized?
Many developing nations and countries have gone for macroeconomic liberalization and spurred balance of payments in the late 20th country. This has happened due to a boost in the global financial transactions.
So, to optimize the landscape of economic boom, developing nations quit restrictions on the transactions of financial and capital accounts. Thus, they took advantage of the capital inflow.
India, a developing economy, can be a classic example in this regard. The country went for a major liberalization of balance of payments in 1991.
The New Economic Policy introduced in 1991 was LPG, meaning Liberalization, Privatization and Globalization.
India, as a nation, reaped most benefits of this liberalization, with more successful integration into the global economy. It also improved foreign investment in the country significantly.
Summing Up
BOP or the the balance of payments is the method of calculating the international monetary transactions of a country within a particular span.
The main elements of balance of payments (BOP) are capital account, financial account and current account.
In an ideal scenario, the current account should be the sum of the financial account and capital account. However, in reality, current account discrepancies remain with variable factors impacting the financial inflow and outflow.