by Abdul Aziz Mondal Automotive Published on: 14 November 2023 Last Updated on: 08 November 2024
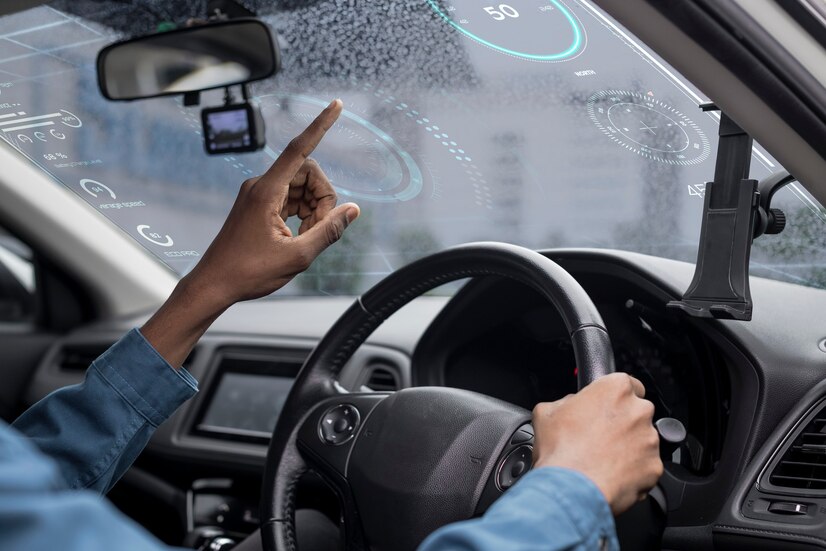

Cars are a big part of one’s everyday life, but have you ever wondered how they go from a concept car to something you can drive? The process often starts with a 3D car design on a computer screen. But getting from that digital image to a real, working car is a big journey. Here’s a look at the key steps.
Step 1: The Idea Phase – Where All Great Cars Start
Before a concept car appears on a screen, there has to be an idea. Designers and engineers brainstorm what they want the new car to do. Should it be fast? Should it save on fuel? They consider what drivers need and what the future of driving could look like.
Once they have a rough idea, they can move on to the next step. This phase is important because a strong concept leads to a strong final product. When the team agrees on the big ideas, they feel more motivated to make them come true.
Step 2: Digital Designing – Making The Idea Visible
It’s time for the designers to get to work. They use special software to create a digital model of the car. This model isn’t just about how the car looks; it’s also about how it works.
The software can simulate how the car will perform on the road, how aerodynamic it is, and even how safe it is in a crash. Some programs, such as the Sonatus vehicle platform, allow automakers to design a modular and flexible software architecture that can support continuous updates and enhancements throughout the car’s lifetime. At this stage, the team will make many changes.
They might decide to move the headlights, change the wheel size, or even adjust the car’s shape to make it better. Digital designing in a concept car lets them see and fix problems early.
Step 3: Prototyping – The First Taste Of Reality
After many digital adjustments, it’s time to build a prototype. This is a physical model of the car, but it’s not yet ready for the road. It might be made of cheaper materials or lack an engine.
But it gives everyone a real-world look at the design. Teams can walk around it, sit in it, and start to see how it fits into the real world. Any issues that weren’t visible on the screen become clear now.
Adobe states, “Imagining a car seat in a photorealistic manner needs the precise creation of its materials. Trim and colors designers have been working every day with color swatches and physical material samples.”
Step 4: Testing A Concept Car – Safety And Performance Checks
Once the prototype looks good, it’s time for rigorous testing. This is where engineers get to see if the design holds up. They’ll put the car through all kinds of conditions — rain, snow, rough roads, you name it.
They’re checking for safety and how well the car performs. If the car passes all these tests, it’s a big step closer to production.
Step 5: Mass Production – From One To Many
The final step is mass production. This is where factories start making many copies of the car so people can buy them. Even at this late stage, small changes might be made to save money or improve the car.
Machines and workers assemble the cars as quickly and as accurately as possible. Only after this stage does the car finally end up in showrooms, ready for people to buy and drive.
Conclusion
Turning a 3D concept car design into a real car is a long and detailed process. It starts with a solid idea and goes through digital design, prototyping, rigorous testing, and, finally, mass production.
Each step is important for making sure the car is not only good-looking but also safe and practical for everyday use. This complex journey shows the care and work that go into every car one sees on the road.
Read Also: