by Pijus Maity Our Blogs Published on: 07 March 2025 Last Updated on: 07 May 2025
There are numerous industries in which heat exchangers play a huge role. From chemical processing and refrigeration to HVAC systems and power plants.
Various industries can benefit significantly from these devices and need them in their operations. What they essentially do is transfer heat between two or more fluids, and that is often essential for different devices and operations.
Now, there are also multiple types of heat exchangers out there, and choosing the right one is important. It affects the overall performance and energy efficiency. And then, it also has an impact on cost-effectiveness.
So, you shouldn’t make any hasty decisions here, and you should, instead, take your time to learn about the different types before making any concrete moves.
What we are going to do today, thus, is talk about the three common types that you should consider when trying to make this choice.
Learning about those is sure to make things a bit easier. And then, we are also going to discuss the process of choosing the right type for you – that is, we are going to talk about what it is that you have to take into account when aiming at making the right choice.
What Are Heat Exchangers?
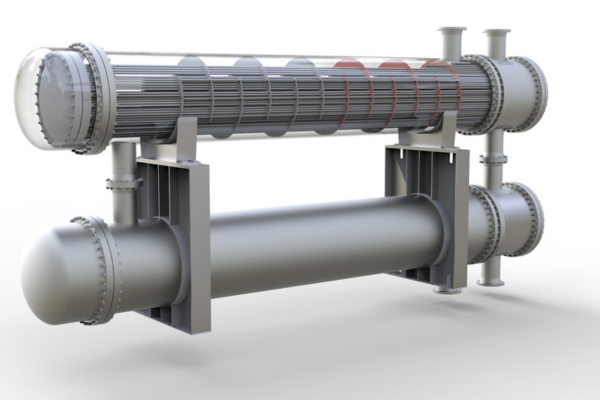
Heat exchangers are devices that exchange or transfer one liquid to another. Due to the diverse applications of a heat exchanger, this device has different names.
So, when you are considering what you need from this device, think about the medium you are planning to cool or heat, and what exactly you are using the same for.
Application Of Different Types Of Heat Exchangers (Industry-Specific):
The different types of heat exchangers are vital in different industries. These devices enable an effective transfer of heat between liquids, improving energy efficiency and performance.
So, let’s briefly look at the different types of heat exchangers and their subsequent applications as per industry.
- Refrigeration and HVAC: Controls humidity and temperature indoors.
- Transportation and Automobiles: Manages thermal batteries in electric vehicles and plays a vital role in vehicle cooling in the automobile industry.
- F&B: Plays a crucial role in controlling temperature in the food processing industry.
- Petrochemical and Chemical Industries: Manages extreme chemical reactions typically involving high-temperature or corrosive substances.
- Power Generation: Heat exchanges help with energy conversion in the power generation industry.
Types Of Heat Exchangers: 3 Common Ones
One thing at a time, though. So, let us begin with the basics. Put simply, let us check out the three types you should consider – the types of heat exchangers you should be aware of whenever you need heat exchangers.
You’ll learn about their advantages, as well as disadvantages, which is, in itself, going to help you make up your mind in the end.
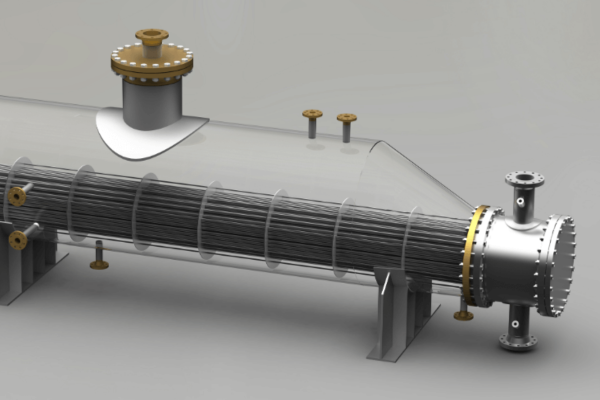
1. Shell And Tube Heat Exchangers:
First off, there are the shell and tube heat exchangers. Consisting of tubes that are enclosed inside a shell shaped like a cylinder, these are among the most common types nowadays. And among the most versatile ones for that matter.
The principle they work on is simple – one fluid flows through the tubes, and another one circulates them, thus making heat transfer easier.
They are suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications and they can handle a wide variety of fluids. Furthermore, they are easy to maintain and clean, and they come with a scalable design ready to meet any of your requirements.
As to their disadvantages, they tend to be bulkier than other designs, which automatically means that they require more room for installation. And, the initial costs of getting them are a bit higher.
2. Plate Heat Exchangers:
The plate heat exchangers are the second type to consider. These consist of multiple thin and corrugated metal plates that are all stacked together. The fluids pass through alternating channels between those plates, thus allowing efficient heat transfers.
Their compact and lightweight design is a big advantage, and so is the fact that they are easy to modify by removing or adding plates, as well as the fact that they require less maintenance than the above type.
Yet, these are not ideal for high-pressure applications, they can be more susceptible to clogging and fouling, and repairs are more expensive in case any of the plates get damaged.
3. Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers:
Next, there are the air-cooled heat exchangers, which use air as the cooling medium, instead of liquids. Consisting of finned tubes and fans, they force the air over the tubes to remove heat.
Given that they don’t require water to work, they are perfect for dry environments, and the costs of operation are also reduced due to the same fact.
They are also environmentally friendly, given that they have a minimal impact on water resources. And, on top of that, they are easy to install, as well as maintain.
On the other hand, though, these require larger surfaces to operate efficiently. So, their efficiency is generally quite limited, especially when compared to liquid-based heat exchangers. And, the fan operation can make them quite noisy.
Type Of Heat Exchangers: How To Choose The Right One For You?
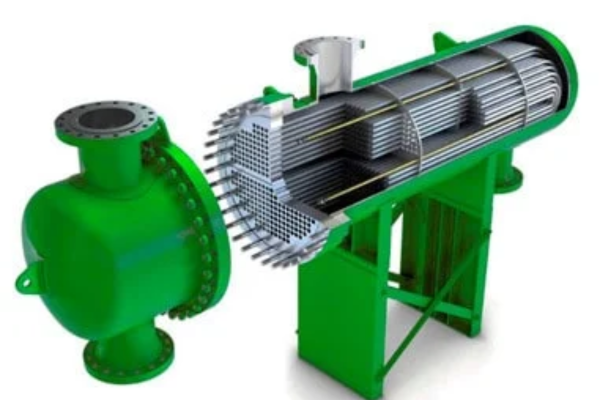

Now, when trying to decide which type is right for you, there’s no doubt that you’ll have to think about what it is that you want to use these for.
When you visit Standard Exchange or similar places, you’ll notice that the shell and tube ones are the most popular, due to their efficiency, stability in performance, and durability.
They are most usually used for power plants, chemical processing plants, oil and gas refiners, as well as industrial cooling systems.
The plate ones tend to be great for HVAC and refrigeration systems, food and beverage processing, as well as the pharmaceutical industry. And the air-cooled ones are great for automotive radiators, as well as refineries, and power generation plants.
Your task is to consider the application, the temperature and pressure condition, as well as the efficiency requirements, and the space and installation constraints.
Furthermore, consider the ease of maintenance, as well as your budget, and then compare everything to make your final choice.